What are Digital Signatures?
Everything you need to know about digital signatures
August 4, 2021
Howdy Howdy,
In this article, I'll be covering exactly what digital signatures are and how they can be used in our ever-expanding digital world.
Let's get started...
Digital Signature Definition
A digital signature is a unique, encrypted electronic brand of approval placed on digital documents such as contracts, emails, or legal statements.
Pros:
![]() Incredibly secure
Incredibly secure
![]() Fast & efficient
Fast & efficient
![]() Authenticity on par with regular signatures
Authenticity on par with regular signatures
Cons:
![]() Some people may doubt the authenticity
Some people may doubt the authenticity
![]() Fee involved in creating your unique signature
Fee involved in creating your unique signature
What Are Digital Signatures?
In the simplest terms, a digital signature is synonymous with an electronic fingerprint.
The digital alternative to signing documents the traditional way – pen on paper or a stamped seal.
The digital signature establishes a secure link between signers and documents in the form of an encrypted message in a recorded transaction.

In addition, they are used to validate the integrity and authenticity of a digital document, message, or software.
Digital signatures revolve around the concept of a standardized format known as Public Key Infrastructure, or PKI, to offer the highest of securities and global acceptance.
They are much more secure than their manual counterparts and were made to eradicate the impersonation and tampering digital communications issues.
Apart from the inherent safety guard, digital signatures provide additional assurances of identity, status, and origin of an electronic document, message, or transaction alongside acknowledging the signer’s informed consent.
Many countries, including the US, consider digital signatures legally binding like conventional document signatures.
How do Digital Signatures Work?
As mentioned before, the digital signature functions based on the concept of public-key cryptography, alternatively termed asymmetric cryptography.
Two keys can be generated by a public key algorithm, like the RSA.
These keys are mathematically linked: one public while the other private.
The two mutually-verifying cryptographic keys are the functioning principles behind digital signatures.
The signer uses their unique private key to secure data related to the signature; the signer’s public key is the only thing that can decrypt that data.
This is how digital signatures and verified.
Digital signature technology asks all involved parties to trust the signer/individual creating the signature can keep their private key secure.
If a party with ill intentions has access to the private key, they can easily make fraudulent digital signatures going by the private key holder’s name.
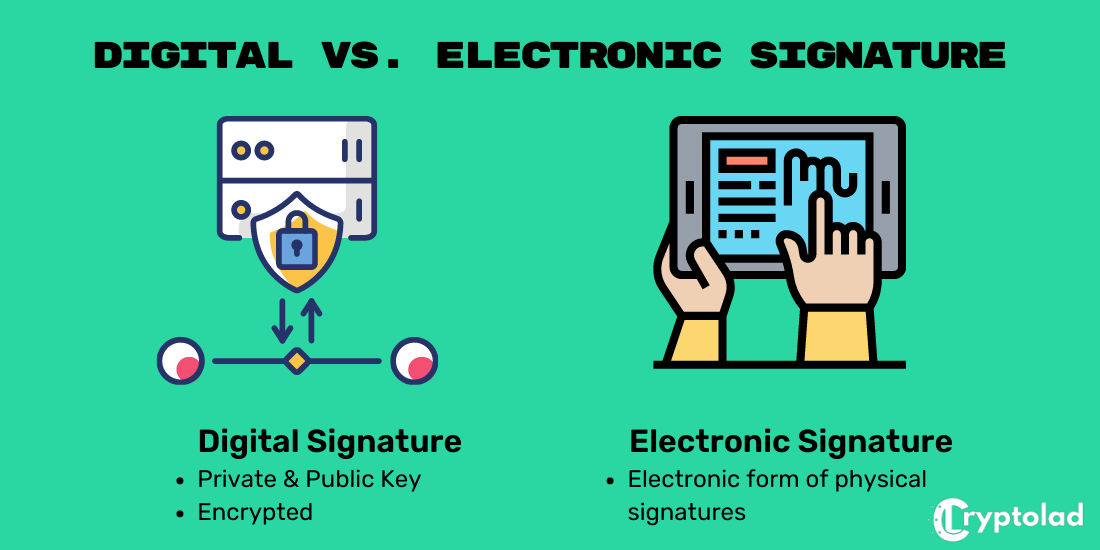
Digital Signature vs. Electronic Signature
Although the terms sound quite similar, electronic signatures are not the same as digital signatures.
A digital signature is mostly a technical term delineating the entire cryptographic process used to verify a data sequence.
In contrast, an electronic signature, otherwise known as an e-signature, is defined legislatively and is a legal term.
For instance, the United States saw the terminology “Electronic Signatures” being defined in the Global and National Commerce passed in 2000.
It was defined as an electronic symbol, sound, or procedure associated with a record or contract and adopted or executed by a person to sign the record.
To break that down, a digital signature can be a kind of electronic signature if it can be expressed digitally and linked with a record’s representation.
An electronic signature has to include three factors to be considered valid:
•A way to authenticate that the signing entity wanted to confirm the document being signed;
•A way to confirm the signing entity’s identity; and
•A way to verify that the electronic signature is truly connected to the signed document.
On its own, a digital signature can meet these requirements to be considered an electronic signature:
•The digital signature’s public key is connected to the identification of the signing entity;
•The digital signature can be attached only by the private key holder of the public key associated with it, which means the entity meant to use the signatures; and
•The digital signature can only verify if the signed document, data, or representation of a document remains unaltered. If the document is changed after the signing, the sign automatically fails to authenticate.
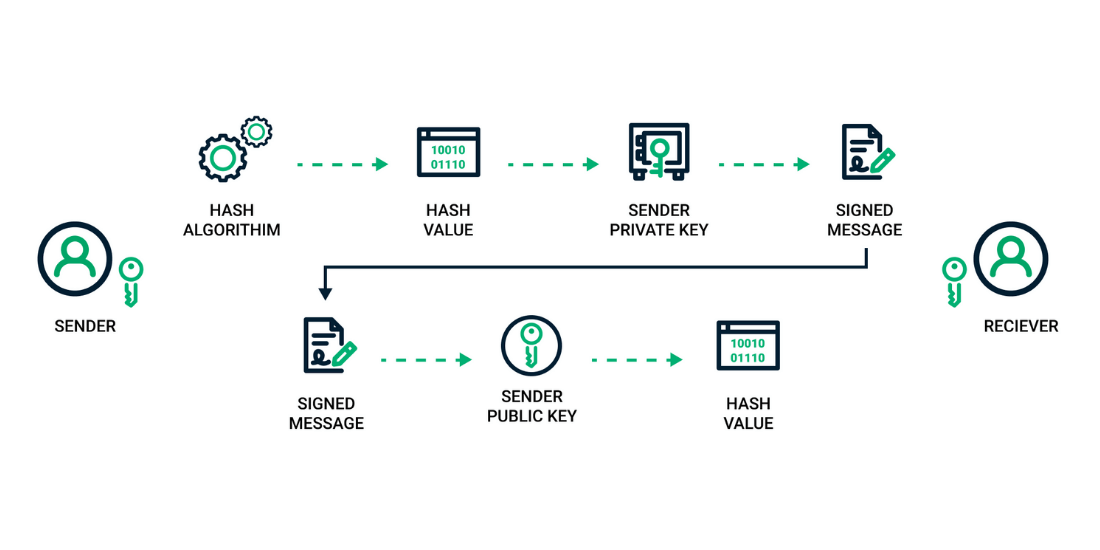
How Digital Signatures are Created
A signing software creates a unidirectional hash of the electronic data that must be signed to create a digital signature.
After this, the private key is used to secure the hash. The encrypted hash and the other information, like the hashing algorithm, are combined with a digital signature.
The hash's encryption but not the whole document or message is because a hash function can transform a disorganized input into one of fixed value, which is generally shorter.
And since hashing takes less time than signing, the process is quicker.
The value of the hash is susceptible to the hashed data. Any minor change in the data will produce a totally different value even of a single character.
When the decrypted hash finds a match within the second computed hash of similar data, it authenticates that it has remained unchanged since the signing.
If the hashes are different, this can mean either of the two: 1. The data has been tampered with, compromising its integrity; or, 2. There has been an issue with authentication as the signature was created using a private key that bears no resemblance to the signer's public key.
One of the biggest benefits of a digital signature is that it makes it difficult for the signing entity to deny signing something – given their private key was secure – since the digital signature is unique to the signer and the document and binds them together. This feature is defined as nonrepudiation.
Keep in mind that digital certificates and digital signatures aren’t the same.
A digital certificate is simply an electronic document containing the issuing certificate authority’s digital signatures.
This binds the public key together with an entity and can authenticate that a certain individual or entity is the public key owner.
The majority of today’s email programs support digital certifications and signatures, making it much easier to sign on any outgoing emails as well as verify incoming messages bearing digital signatures.
Digital Signatures in a Nutshell
The main purpose of a digital signature is to provide proof of data integrity, authenticity, as well as nonrepudiation of transactions and communications conducted online. It is safe to say that it is the future of records as technology establishes a firmer grip over the world.
Happy trading!
New to Cryptocurrency? Read our free beginner guide!